Dissociated Oxygen Saturations
by Dr Paul Young, last update March 16, 2019
aka Hematology Hoodwinker 004
One of the emergency residents has just taken an ABG on the 44 year-old woman in cubicle 3. Prior to her current presentation she had no known medical problems. The patient’s pulse oximetry reading is SpO2 98% on air.
急诊科的一名住院医师刚刚为一名44岁的女性患者做了动脉血气检查。此次发病前,患者没有既往病史。患者吸空气时脉搏氧饱和度(SpO2)为98%。
This is the arterial blood gas:
患者动脉血气结果如下:

Questions 问题
Q1. What are the possible explanations for the discrepancy between the pulse oximetry reading and the oxygen saturation on the arterial blood gas?
Q1. 脉搏氧饱和度与动脉血气氧饱和度结果不一致的可能原因有哪些?
A1. Answer and interpretation
A1. 回答与解释
Possible explanations for ‘pseudo-hypoxaemia’ include
假性低氧血症的可能原因包括
- Equipment failure
— faulty pulse oximeter
— faulty blood gas analyser - Blood sample used was actually venous
- Blood sample taken from a site affected by localised hypoxemia, e.g. ischaemic limb
- Excessive oxygen consumption following blood sample collection (e.g. massive leukocytosis or thrombocytosis)
- 设备故障
— 脉搏氧饱和度仪错误
— 血气分析仪错误 - 使用的血液标本为静脉血
- 采取血液标本的部位受到局部低氧血症的影响,如肢体缺血
- 血液标本采集后过度氧耗(如严重的白细胞增多症或血小板增多症)
Dyshemoglobinemia can also cause a discrepancy between SpO2 and SaO2, but will not cause the decrease in measured PaO2 as seen in this case.
异常血红蛋白血症也可以导致SpO2 与 SaO2 不一致,但不会引起本例看到的PaO2降低。
- In carbon monoxide poisoning SpO2 will read in the 90s despite high levels of COHb — but the PaO2 should still be high.
- In methemoglobinemia, the SpO2 plateaus at about 86% with increasing levels of MetHb, but again the PaO2 will not be decreased.
- 一氧化碳中毒时,SpO2可能仅为90%,尽管COHb水平很高 — 但PaO2 仍然应当很高
- 高铁血红蛋白时,随着MetHb水平不断升高,SpO2在86%达到平台,但PaO2同样不会降低
Q2. What other blood test would be particularly helpful?
Q2. 其他哪些血液检查结果会有帮助?
A2. Answer and interpretation
A2. 回答与解释
The full blood count
全血细胞计数
This is what the patient’s blood test showed:
以下是患者血液检查结果:
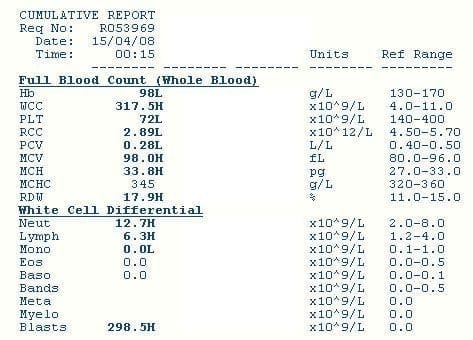
Q3. Describe the blood test result shown in Q2?
Q3. 请描述Q2中血液检查结果
A3. Answer and Interpretation
A3. 答案与解释
The key findings are
主要发现为:
- massive leukocytosis, due to a large number of blasts
- normocytic anemia (Hb 98 with normal MCHC), mild macrocytosis (MCV 98) and increased RDW (17.9)
- thrombocytopenia
- 因为大量母细胞造成的重度白细胞增多症
- 正常细胞性贫血(Hb 98且MCHC正常),红细胞轻度增大(MCV 98),RDW升高 (17.9)
- 血小板缺乏
Spurious hypoxaemia in this setting is also known as ‘leukocyte larceny’.
本例中假性低氧血症也被称为“白细胞盗窃”。
Q4. Interpret the blood test result shown in Q2? What is the likely underlying diagnosis?
Q4. 解释Q2中血液检查结果?最可能的诊断是什么?
A4. Answer and Interpretation
A4. 答案与解释
Acute myeloid leukemia
急性髓系白血病
Hyperleukocytosis (>100 x 10E9/L) is almost always due to a hematological malignancy.
白细胞增多 (>100 x 10E9/L) 几乎总是由于血液系统恶性肿瘤造成。
Blast cells in the blood suggest acute leukemia or a blast cell crisis. The presence of Auer rods in the blast cells would confirm the diagnosis of acute myeloid leukemia. Blast cell crisis occurs when chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) undergoes transformation into a more aggressive condition.
血液中的母细胞提示为急性白血病或母细胞危象。母细胞内发现Auer小体可以确诊急性髓系白血病。慢性髓系白血病(CML)发生急变时即可出现母细胞危象。
Blast cells are immature precursors of either lymphocytes (lymphoblasts), or granulocytes (myeloblasts). They do not normally appear in peripheral blood. They can be recognized microscopically by their large size and primitive nuclei (ie the nuclei contain nucleoli).
The anemia and thrombocytopenia is consistent with bone marrow failure.
贫血与血小板缺乏与骨髓功能衰竭相符合。
Q5. What other complications is this patient at risk of?
Q5. 此例患者还可能出现什么其他并发症?
Q6. What are the treatment options?
Q6. 治疗选择有哪些?
Q7. How could the abnormal blood gas result be avoided?
Q7. 如何避免得到异常血气结果?